Lesson 2: Introduction to Appreciative Inquiry
Description
Lesson Two Objective
In lesson two our objective is to build an understanding of an Appreciative Inquiry (AI) process and how it works in practice.

Introduction
In Lesson One we began our course objective to demonstrate how Appreciative Inquiry (AI) can transform our approach to just about anything including this state of feeling strong while job finding. This is a simple technique with a complex background covered in Lesson One where we set the context for Appreciative Inquiry (AI), our first agenda item.

The photo is a moment of the movie Karate Kid that you will recall that before the young boy, Mr. Macchio in photo, can become karate master he needed to gather the foundational skills. His enthusiasm decreased when instead all summer the karate master, Pat Morita in photo, had the kid just waxing his car as demonstrated in the photo versus teaching him the extraordinary schemes and moves he was expecting. Unknowingly, the waxing techniques were secretly teaching his muscles karate moves, and when the karate lessons actually began, he found it relatively easy to learn. Hence, Lesson One is a little bit of the wax on, wax off approach that I think you'll find in this course will result in lightbulbs of application surprisingly efficient now that you have context for AI.
I think the moral of wax on, wax off is not unlike AI. People can be enthusiastic about future plans, it is best to not start the path of plans with preconceived ideas. First take some time to notice your past and present successful experiences, environment, surroundings and the elements around them. Understand that there's a lesson in every element. Become more aware of the value and significance of positive details and understand that seemingly insignificant things are the bricks that build the wall of success, for there's a lesson in every layer. This is how AI works one stage at a time, each step building on the last.
AI has been used productively all over the world to consult with people and learn from their experiences, to involve a whole community in change and development and to build a vision for the future that everyone can share and help put into practice. In this course you take yourself through the steps to empower yourself in ways of staying strong and resilient in job hunting to build and live your own vision of the future. In lesson two we prepare you further to set you up for success when you put AI into practice lessons 3 and 4.
Recap:

Recall that Appreciative Inquiry is a methodology built on existing principles and developed by Professor David Cooperrider and his colleagues at Case Western Reserve University developed in the 1980s, in Chicago. The following explanation of Appreciative Inquiry (AI) is taken from his ‘Imagine Chicago’ initiative to now connect our previous context learning of AI into Lesson Two and commence how AI works in practice.
In Appreciative Inquiry (AI):
1. You appreciate what is by discovering and valuing those factors that give life to you; for example, what do you value most about yourself, your neighbours, your school, the community organizations of which you are a part? What in your view is making a positive difference to your quality of life? What contribution are you/have you made/making that you are especially proud of?
2. You envision what might be. When the best of what is has been identified and is valued, the mind begins to search beyond, to dream new possibilities. Imagining involves "passionate thinking", allowing yourself to be inspired by what you see. It means creating a positive image of a desired future. E.g. what small outreach project would make a big difference on your block?
3. You construct a vision that involves engaging in dialogue with yourself or others, discussing and sharing discoveries and possibilities. Through internal or external dialogue, individual vision becomes a designed blueprint for a shared future vision.
4. You sustain your ideals by creating the future through innovation and action. Because ideals are grounded in realities, there is confidence to make things happen and hence destiny.
How Appreciative Inquiry [AI] Works
“A manual of strengths and virtues that are found in the happiest people" (Peterson & Seligman, 2004)
The Language We Use
We learned with the constructionist principal that spoken words create meaning and future realities so this creates an importance in the language we use in AI. We learned the moment we ask a question and inquire simultaneously we create change. Our image of the future drives our ACTION! When individuals, organizations or groups capture positive imagery internally and make it visible, it starts to drive and change in an individualistic, self-directed way. It creates a sense of focus. Please consider these research effects and revolutionary fields.
Pygmalion Effect;
Change a teacher’s image of a student, and their behavior changes toward the student, improving student performance.
Internal Conversations;
In studies of pre and postoperative patients there is a difference in recovery between positive and negative imagery.
Placebo Effect;
Help someone construct an image of how something might happen, and it drives behavior which creates a change in that direction.
Sociology;
The study of problems creates an increase in number and severity of problems. Good news is the opposite also occurs.
Nexus of Three Revolutionary Fields
Appreciative Leadership is the joining of Three Revolutionary Fields: Strengths Movement, Positive Psychology and AI.
Movement;
Sports or Strengths Movement provides great credence to the impact of vivid visualization of one’s performance that actually guides physical performance. What research tells us now is that the speed of learning is expedited when only correct images are reviewed.
Positive Psychology;
“Authentic Happiness: Using the New Positive Psychology to Realize your Potential for Lasting Fulfillment” Abraham Maslow
Conventional Psychology tends to be about negative things e.g., anxiety, depression, stress, etc…Positive Psychology attempts to redress the balance, to try to contribute to positive aspects of life. Recall the positive principle the positive effect leads to positive action.
Positive Emotions lead to Positive Actions
Joy leads to play, innovate
Interest leads to expansive, explore
Content leads to savor, integrate
Love leads to connect, relate
Confidence leads to innovate, create

Appreciative Inquiry (AI)
Similarly Questions are fateful. Human systems move in the direction of what they most frequently and persistently ask questions about. What you study, GROWS! What does our media focus on? What will the amplification of fear teach us about joy and love? What does your leadership style emphasize? How does that impact innovation and collaboration?
"The most serious mistakes are not being made as a result of wrong answers. The truly dangerous thing is asking the wrong question." Peter Drucker
There is a photo in summary to explain the language we use in AI that has a background close-up of the commencing transformation of the fall seasons with beautiful yellow, red and hint of green in the leaves. The fall trees are overlaid with some white lettered content Cooperrider and Whitney noted, which is as follows:
What we ask determines what we discover. With an emphasis on the word ask and discover.
What we discover determines how we talk. With an emphasis on discover and talk.
What we talk about determines how we dream together. With an emphasis on talk and dream.
How we dream together determines what we design and create together. With an emphasis on dream and design and create together.

What’s Different about AI?
Purposefully positive
Builds on past success to create future success
Emphasis on image and language
Nurtures a positive “inner dialogue”
Highly participative
Accelerates change

Working Assumptions of Appreciative Inquiry [AI]
There are eight Assumptions of Appreciative Inquiry we will explore. The base assumptions of Appreciative Inquiry [AI] affect the change process and you may have experienced them already in our individual lives.
- In every society, organization, group, or family something works.
- What we focus on and the language we use becomes our reality; Positive image, positive action. It comes down to the choices we make. The invitation is to be fully conscious all the time. Do we inquire into low morale or times of heightened enthusiasm? What is the most motivating way to create novelty and innovation? How do we foster inclusiveness?
- Reality is created in the moment in conversations, and there are multiple realities. The language we use creates our reality; the stories we tell, are the stories we live.
- The act of asking questions of an individual, organization or group influences the group in some way. Even questions we pose to ourselves as individuals influence the way we think.
- People have more confidence and comfort to journey to the future (the unknown) when they carry forward parts of the past (the known).
- If we carry parts of the past forward, let it be what is best about the past.
- Embrace differing perspectives.
- Strength-based development engages the heart and frees the human spirit.
Adapted from Sue Annis Hammond, (1998) 2nd Edition. The Thin Book of Appreciative Inquiry Plano, Texas: Thin Book Publishing Company, 20-21.
Determining the Internal Dialogue
“The greatest discovery of my generation is that a human being can change his life by changing his attitude of mind.” William James


In memory, stories, and imagination there are resources that enable an individual to shape the way dialogue is read and the choice of reading affects how change comes about. How this information is interpreted is a person’s internal dialogue.
If these images are out of step, the individual will experience them self as dysfunctional and rational attempts to fix them self will not work until the underlying affirmative image is changed.
Fundamentally, an individual’s affirming image is the most important aspect of change potential as nothing the ‘rational mind’ decides it wants will happen if the ‘inner dialogue’ is resistant to it.

Appreciative Inquiry is founded on a set of ‘life affirming’ beliefs about people and human organizing:
Appreciative Inquiry is inherently optimistic, and assumes every single person has capacities, abilities, unique gifts, skills and contributions to bring to life. The strength of the individual or the community is directly proportional to the level that the person wants, and is able to contribute their abilities and assets to their well-being.
Individuals, organizations and communities are sources of unlimited relational capacity, created and lived in language. For example focus on the resources and capacities of a community and its residents, instead of dwelling on their needs problems and deficiencies.
The images we hold of the future are socially created and, once articulated, serve to guide individual and collective actions. Appreciative Inquiry believes that meaningful and lasting community or individual change always originate from within, and individuals for themselves or local residents in the community are the best experts on how to activate that change.
People can shift their attention and action away from problem analysis to lift up worthy ideals and productive possibilities for the future through human communication of inquiry and dialogue.
In short, Appreciative Inquiry (AI) suggests that human organizing and change, at its best, is a relational process of inquiry, focused on ‘what we want to realize’ and grounded in affirmation and appreciation of what works well – the “positive core” of strengths.
Positive Core; the Essence of Appreciative Inquiry (AI)
![There is a picture of the simple cartoon flower. The stem at the center of the flower have the purple coiling words, ‘Positive core.’ Branching off of the positive core flower stem are four leaves going top to bottom titled: discovery [in bluish purple], dream [in reddish purple], design [in rustic blue] and destiny [in baby blue]. The intention of the flower picture is symbolic of how a positive core flower stem feeds it leaves, and vice versa. The leaves nourish the positive core stem.](http://s3.amazonaws.com/tigfiles/images/tiged/upload/936925/56cc9e9d44a3f.png)
Appreciative Inquiry (AI) works on the assumption that whatever you want more of already exists in all systems. What we seek is waiting to be discovered, the seed is there, Appreciative Inquiry (AI) waters it.
In a nutshell, Strength Based Curiousity of Appreciative Inquiry (AI) seeks to release the positive core of a person, an organization, or a community by amplifying or blooming what is working well.

The applicability of the Appreciative Inquiry model is not limited to an individual. It can also be effective for small groups as well as large-scale summits, or even for families and relationships. The point is that wherever there are people, there is always an opportunity to focus attention and energy on the natural strengths and assets of that group or individual.
Positive Core Examples
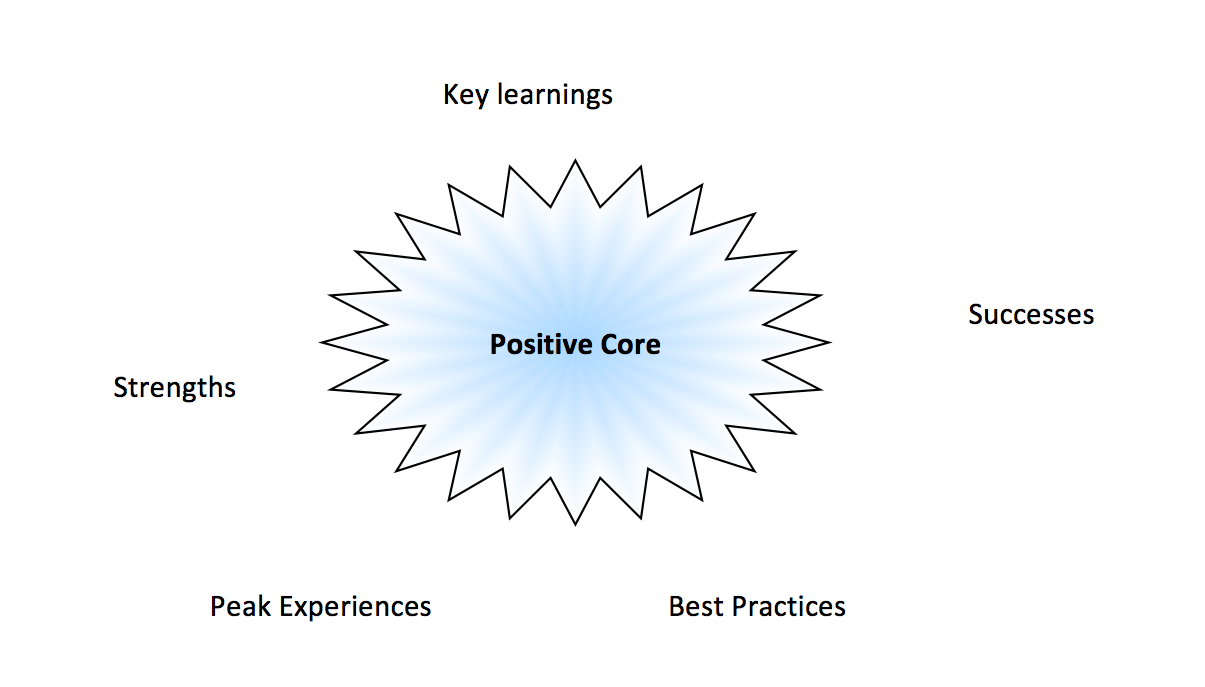
Connection to the Positive Core
Elevates
Positive emotions of hope, inspiration, confidence, joy.
Increases
Creativity, better decision making, increased collective capacity.
“Undoes”
Negative impacts - letting go, makes irrelevant, finishes the residual of negative past.
Protects
Increases health-ability; resilience; accumulation of power; like an increase in immune system functioning.

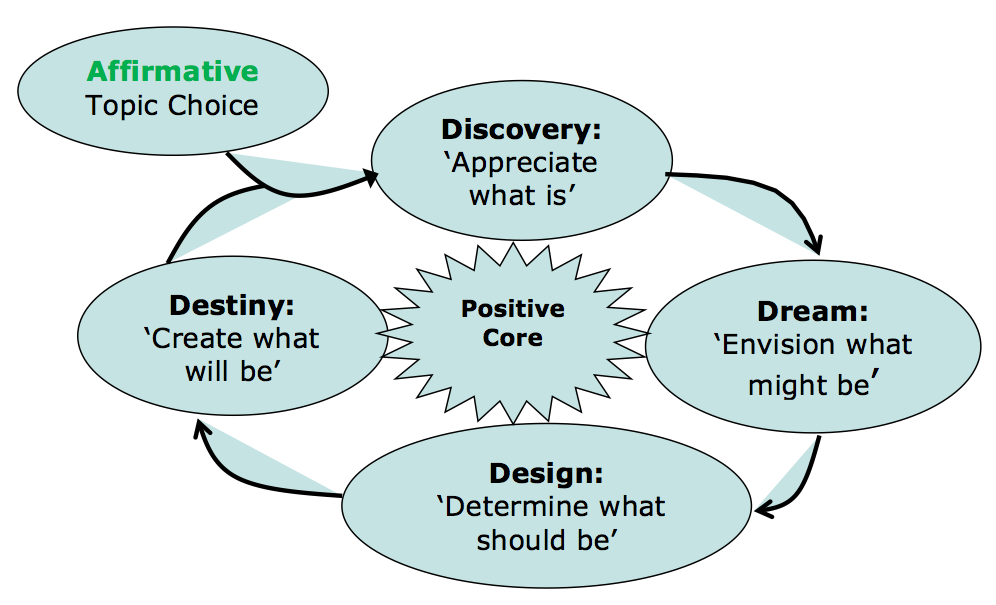
Affirmative Topic Choice
Our work begins with the thoughtful identification of what is to be studied; affirmative topics. What is a compelling strategic focus or change agenda; an affirmative topic choice that is something of significance that you hope to realize. In an organization or a group affirmative topics could include “inspired leadership,” “optimal margins,” or “culture as competitive advantage.” For individuals there are examples such as: Happiness at school, ways to becoming blissful, ways to the state of relax, transformation of leadership style, or ways to the state of “feeling strong.” At the heart of the AI process is customized inquiry. Since human systems move in the direction of what they study, the choice of what to study; what to focus organizational or individual attention on, is both essential and strategic. The topics that are selected provide a framework for collecting stories, discovering and sharing best practices, and creating a knowledge-rich work environment. They become the organization or individual’s agenda for learning and innovation.

Characteristics of Good Affirmative Topic:
Topics are positive. Topics are desirable. Topics stimulate learning. Topics stimulate conversation about desired futures (preferred futures).
‘Ways to the State of Feeling Strong ‘Affirmative Topic Choice
For the purpose of this course the focus will be around resilience. The skill of framing and re-framing the affirmative topic choice is important as it guides the Appreciative Inquiry (AI) Process. So we reframed resilience to an ‘Affirmative Topic Choice’ to be ‘Ways To The State Of Staying Strong’ in the job hunting process. Human systems move in the direction of what we deeply and persistently ask questions about. Transformational topics are possible in any situation, and will generate more positive change every time.
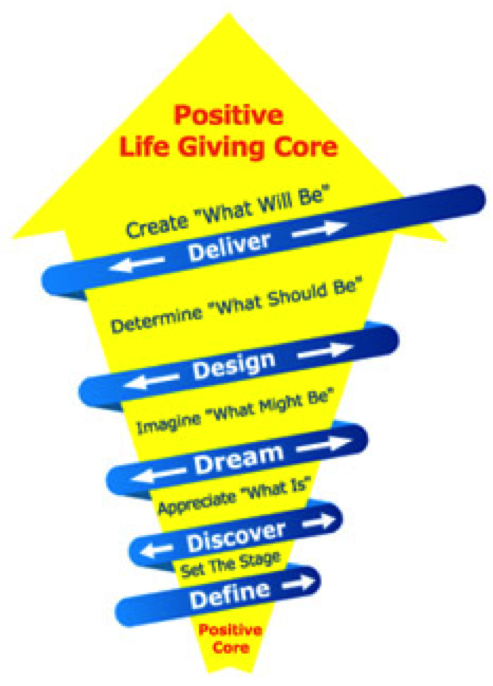
4-D Process of Appreciative Inquiry
Cycle Introduction
As the name implies the 4-D has four stages that form a cycle – Appreciate, Envision, Construct and Sustain. These are sometimes known as Discover, Dream, Design and Destiny - the 4-D cycle. We provide you with a defined Affirmative Topic Choice ‘Ways To The State Of Staying Strong’ to generate positive results with the Appreciative Inquiry 4-D Process. The 4-D AI process enables us to direct the attention and dialogue on its most powerful potential; its positive core. Recall every person has a positive core that include; successes, peak experiences, key learnings and best practices. The positive core is the essential nature of you at your best; your collective wisdom, tangible and intangible strengths, capabilities, resources, potentials and assets. This 4-D technique is just one of the Appreciative Inquiry methods.
The Appreciative Inquiry 4-D Process unleashes the energy and ideals of the ‘Positive Core’ for transformation and sustainable success. ‘Affirmative Topic’ selection begins the adventure into Appreciative Inquiry (AI). It requires searching for the positive description of what is desired. Because individually we move towards whatever we study, the selection of the AI topic is critical. It is the foundation of the entire process. Hence, the topic choice process is to be an affirmative act that evokes conversations of the desired future. In this course the affirmative topic choice reframed resiliency to be ‘Ways To The State Of Staying Strong.’
The Four Steps to Appreciative Inquiry from discovering an appreciative question, to dreaming of a future state, to designing a provocative proposal and manifesting a destiny, each step is crucial to the process of Appreciative Inquiry. We get to incorporate the “buzzwords” of the last decade, Innovation, Empowerment, Continuous Learning, Partnership, and Making a Difference, into a process of change that is FUN! Imagine the possibilities!
Badges high level overview

AI 4D Stage Badges in the course:
- Discovery Identifying your Positive Core List
- Dream Images of Future Visions
- Design Provocative Possibility Propositions for Ideal Future
- Destiny Step by Step Actions/Projects for Continuous Learning
The Four Stages
Discovery/ Appreciate
“No pessimist ever discovered the secret of the stars or sailed an unchartered land, or opened a new doorway for human spirit.” Helen Keller

The key is to seek out the positive, life-giving forces within each system and to appreciate the best of ‘what is.’ In AI, we are seeking to identify and acknowledge the value within a system. Each participant in this course will begin the process by taking an appreciative position regarding their own contribution to their own destiny.
Discovery is about finding what type of processes, past successes and skills work for you and will help you along your way. It is also a process of learning to appreciate what has been given to us and using it to our benefit. In the Discussion Section it is recommended the course Students and Job Seekers discover some of this information by speaking with other students and Job Seekers and learning about what has worked for them in the past. This can lead to feeling more appreciative about your contributions and what you can share to make meaningful contributions.
Discovery Examples:
Conversing with others about your experiences
Asking managers what interviewees have won them over in the past
Observing your past actions that have been successful
Discovery stage is about finding out what has worked in the past. It seeks to find out people’s best experiences; experiences they are enthusiastic about and proud of. So as well as collecting information, this stage is typically also about involving people and building on their natural enthusiasm. The main approach for this stage is conducting appreciative interviews and in this course are mostly self-reflective appreciative interviews though students are encouraged to reach out and interview beyond the badge exercises of this course.
An organizational example: As part of the Imagine Chicago initiative, fifty at -risk young people, accompanied by adult mentors, interviewed 140 business, civic, and cultural leaders. The leaders shared high points of their lives as citizens, their hopes for the city’s future, and effective processes for getting people in the city working together. The program culminated in a day-long imagination celebration at Preston Bradley Hall which involved both the interviewers and their interviewees to distill the learning and rally people’s commitments.
Dream/Envision

The dream phase focuses on what would work for you in the future. This ‘dream session’ can be run in a large group conference or can be done with a few peers or individually. Either way, it allows everyone to open up about what they want to see and any ideas they may have for improvement. The idea of the ‘dream’ part of this model is to use positive energy to create a vision for the future, while creating goals and accomplishments that will help you reach that point to Dream up the ideal and perfect situation.

Dream Examples:
“Would this work in the future?”
“What do I want to see happen?”
“What would be perfect for me?”
This stage is about moving from the past to the future. Having discovered best practice examples from the past and identified what made them work, we now look to the future - how we can recreate these good experiences and build on them? What would we like to see for the future? How do we want things to be?
An organizational dream example: The New Economics Foundation carried out an “Imagine Planet” project using Appreciative Inquiry. One lady was very upset about the dumping of rubbish in front of her flat days before the rubbish collection was due. When asked in an AI way, she recalled a time when residents used to remind one another about collection day, and would help less able residents to carry their rubbish out. This became her vision for the future within her tower block.
Design/Construct

The design plan is all about how you plan to reach the goals and dreams that were lined out in the discovery and dream phases. This part of the model focuses on what needs to be done to reach these goals and reach the progress needed. You are encouraged to remember to use positive language and to think positive in your work.
Design Examples:
“What do we need to do to make this happen?”
“Will things needed to be changed or altered?”
“Do we need to introduce a new element?”
This stage is about the present. How can we move from where we are now to this vision of the future that we have created? How can we put the ideas into practice? Who will be involved?
Organizational Design Example: The International Institute for Sustainable Development worked with Skownan First Nation (Canada) on a consultation to integrate aboriginal values into strategies for land use and resource management. After carrying out a series of appreciative interviews, the team staged six data analysis workshops and six community workshops, open to all members of the community, to prioritize the results and to develop a community strategy and action plan. They also held two focus group meetings to communicate the results to key decision makers in the public and private sectors. .
Provocation affirms the notion that people are capable of becoming more than what they currently are. Every person inherently has the potential to improve. Provocation means inviting you to take some risks in envisioning your future. This means encouraging new ways of thinking and bold dreams of what you might become. So we provoke you to think radically and outside the box in order to arrive at new visions for yourself.
Destiny/Sustain
Our destiny changes with our thought, we shall become what we wish to become, do what we wish to do, when our habitual thought corresponds with our desire. Orson Swett Marden
The destiny phase, sometimes called the delivery phase, is the final stage of the Four D model, and focuses on executing the plans and ideas that were thought out and developed in the previous phases. In this part of the model, students need to take the necessary actions to progress toward change and positively obtaining their goals. A plan isn’t worth the paper it is written on if it doesn’t get carried out.
Examples:
Implement any changes needed
Remove elements that no longer work
Action on tasks and duties as needed
This stage is about putting it into practice and allowing the ideas to flourish and develop. Traditional project planning and management tools might be used, but above all there must be a willingness to allow for change. There is also an emphasis on empowering and encouraging you to take forward your own ideas. This is very close to traditional ideas of capacity building.
Example: In the US telecommunications firm GTE, an Appreciative Inquiry initiative eventually led to a Statement of Partnership between the company and the unions stating, “The company and the unions realize that traditional adversarial labor -management relations must change to adapt to the new global telecommunications marketplace … the company and the unions have agreed to move in a new direction emphasizing partnership.” This was even more significant because the unions had tried at first to close the initiative down.
For further details, please see the Imagine Chicago website http://imaginechicago.org
Application means that the knowledge and insights generated by an inquiry should be applicable toward actions that can move you forward. Dreaming about all the possibilities can without a doubt be fun and exciting. But getting seduced by unattainable fantasies will not help to transform an organization. Not every individual will invite an idea and end up running a company to get to be the size of Microsoft. Not every non-profit will completely eradicate the problem to which they are dedicated to confronting. And not every sports team will shut out its opponents in every match. The ideas that are spawned during an AI process should eventually lead to agreed-upon actions that can ultimately be implemented in your world. Overall, this principle of application ensures that the AI process remains grounded in reality.
Conclusion

Applying Appreciative Inquiry of the positive questioning is the defining allurement, like the sun in the Heliotropic Principle. What you focus on grows. The act of inquiring appreciatively is the driving vehicle in Discovering, Dreaming, Designing, and ultimately your Destiny. AI can not only transform individuals and/or organizational processes but does so in a way that becomes self-nourishing and therefore sustainable in the longer run.
Every person/organization has a positive core no matter how bleak it includes; successes, strengths, peak experiences, key learnings, best practices and when people focus on positive core you bring it to light. ‘Affirmative Topic’ selection begins the adventure into Appreciative Inquiry (AI).
Task
Create a two question quiz for Lesson 2. Feel free to use these Tools:
Testmozis an app that lets you create an online, self-correcting quiz without having to register.
Jeopardy Labs lets you easily create an online Jeopardy game without having to register. I recommend ignoring the site’s instructions and just writing the questions first and the answers second so that the board displays the question of course which ever you prefer is up to you.
Discussion 2 Complete another person[s] posted quiz[es] 4 questions other than your own
Positive Core Identified
Appreciative Inquiry proposes that within every human grouping or system, people have experienced periods of exceptional performance and achievement, and moments of connectedness, meaning, and joy. They have also been stirred and energized by visions of a valued and positive future. These times of extraordinary success and inspired feelings often tend to be forgotten. They can get swallowed in the day-to-day grind, and lost in the seemingly relentless cycle of “damage control.” So Appreciative Inquiry creates a framework for systematically recalling the behaviors, attitudes, and emotions that were present during these “peak experiences” or exceptional achievements. It asserts that it is through the exploration of “what has gone right” that new insights can be arrived at.
Pick 1 of the 2 task choices to complete for generating thoughts about your Positive Core:
A] Positive Core Map example in photo


Tools you can use:
Post a photo of your hand made creation
Create an online poster withTackk. FYI They’ve just announced aspecial education pagewith class-related templates and examples.
UseDvolver Moviemakerto create short animations with text bubble dialogue. You can see many examples of these films on myExamples of Student Workpage.
Create a cartoon atMakeBeliefsComixand theToronto Public Library Tell-A-Story Builder.
OR
B] Positive Core: “That which makes up the best of you”
The following are some of the ways in which the positive core can be expressed. Think about a time and give an example that demonstrates strength in each of these areas (or as many as possible). For Badge One in Lesson Three you will need a story that demonstrates strength that can be inspired from completing this initial activity.
Success _____________________________________________
Strength _____________________________________________
Peak Experience _____________________________________________
Key Learning _____________________________________________
Best Practice _____________________________________________
Achievements and awards _____________________________________________
Innovations _____________________________________________
Leadership _____________________________________________
Positive emotions _____________________________________________
Product superiority _____________________________________________
Service superiority _____________________________________________
Relationships _____________________________________________
Vision _____________________________________________
Technical strength _____________________________________________
Vital traditions _____________________________________________
What are other strengths that you might list as part of your positive core: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________
Continue to Lesson 3: The “Art” of the Positive Question »
Submissions (1)
-
Tania Rashid Discussion post: 3634.1 days ago

